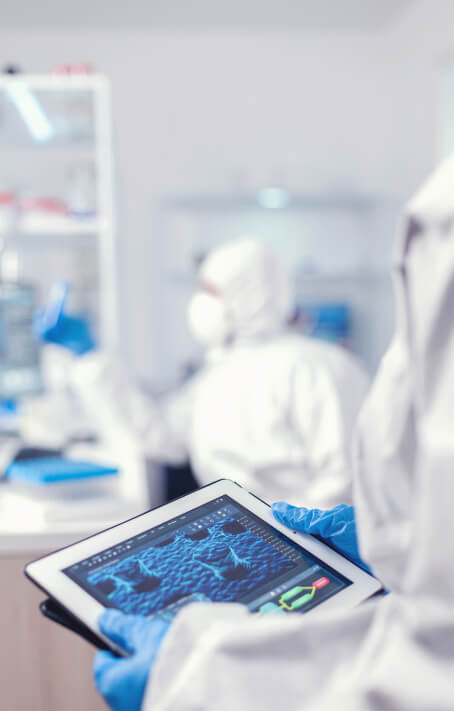
QMS Review & Implementation
Pharmaceutical Quality Management System (QMS) is a comprehensive collection of policies, processes, and procedures designed to ensure and maintain uniform and high quality in the production of pharmaceutical products.
The QMS must reflect the specific needs of the pharmaceutical company and applicable regulatory requirements.
A robust Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS) that reflects the applicable requirements can also help pharmaceutical companies to mitigate risks, improve customer satisfaction, and streamline quality processes.
The pharmaceutical quality management system includes several processes, such as:
- Document management
- Change control
- Training management
- Audit management
- CAPA management
- Deviation management
- And others
QMS Implementation & Optimization
-

Designing and Implementing Document Control Systems
- Develop and establish robust document control systems to manage all GMP-related documentation.
- Ensure secure storage, version control, and easy retrieval of documents.
-

Establishing Robust Change Control Processes
- Develop change control procedures to manage and document all changes to processes, systems, and equipment.
- Train staff on change control protocols to ensure compliance and minimize disruption.
-

Continuous Improvement of Qms
- Use GAP analysis and performance metrics to identify areas for improvement in the QMS.
- Implement corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) to address identified issues and enhance system performance
Critical Events Management
-

Deviations
- Develop and implement a system to efficiently capture, categorize, and manage deviations.
- Use root cause analysis to identify underlying issues and implement corrective actions.
- Regularly review deviation data to identify trends and patterns.
- Use trend analysis to proactively address recurring issues and improve processes.
-

Complaints
- Establish clear and effective procedures for receiving, documenting, and investigating customer complaints.
- Ensure timely and thorough investigation of complaints to determine root causes.
- Implement corrective and preventive actions to address issues and prevent recurrence.
- Use customer feedback to inform continuous improvement efforts.
-
Out Of Specification - OOS
- Develop procedures for promptly investigating and documenting OOS results
- Conduct a thorough root cause analysis to determine the reasons for OOS results.
- Implement corrective actions to address the root causes and prevent future occurrences.
- Regularly review and analyze OOS data to identify trends and areas for improvement
Document Elaboration
-

Sops, Forms
- Develop and maintain detailed SOPs to ensure consistent and compliant execution of all GMP-related activities.
- Design and implement standardized forms for recording data and documenting processes.
- Ensure forms are user-friendly, comprehensive, and compliant with regulatory requirements.
-

PQRs, VMP, QMR
- Analyze data from production, quality control, and stability studies to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Develop a VMP to outline the overall validation strategy and approach for the organization.
- Review key performance indicators (KPIs), audit findings, deviation trends, and other quality metrics.
-

Contamination Control Strategy (CCS)
- Create a detailed contamination control strategy to prevent, detect, and mitigate contamination risks in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Include strategies for environmental monitoring, cleaning and disinfection, personnel hygiene, and equipment design.
- Document monitoring results and use findings to improve the CCS.
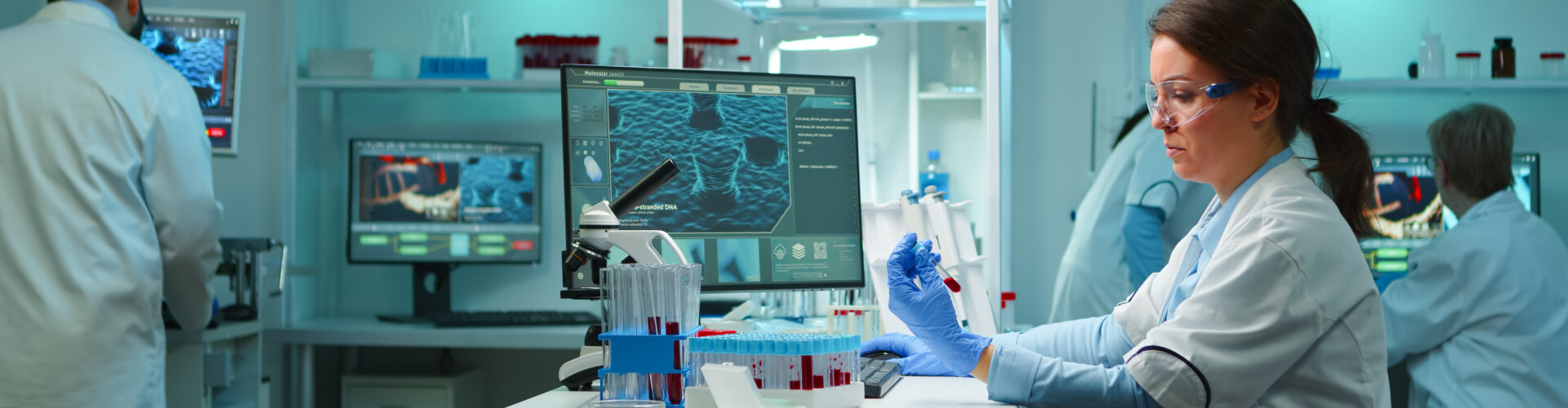
Risk Management
-

Identifying Potential Risks in Processes and Products
- Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential risks in all processes and products.
- Utilize tools such as Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), and risk matrices.
- Create detailed process maps to visualize and understand workflow and identify points of potential risk.
- Analyze historical data to identify recurring issues and trends that could indicate potential risks.
-
Implementing Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Create detailed risk mitigation plans outlining specific actions to reduce identified risks.
- Prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood, focusing on high-risk areas first.
- Implement preventive measures such as process improvements, enhanced training programs, and stricter quality controls.
-
Monitoring and Reassessing Risks Regularly
- Implement continuous monitoring systems to track the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies.
- Use real-time data and analytics to detect and respond to emerging risks promptly.
- Conduct regular audits and reviews to assess the effectiveness of risk management activities.



 Copyright GAMP Services 2024. All Rights Reserved.
Copyright GAMP Services 2024. All Rights Reserved.